Ben Leffew, Preserve Manager
Laura Baird, Assistant Preserve Manager
Bats are an integral, but often overlooked and always misunderstood, part of our ecosystem. These small flying mammals eat their body weight in insects every night, making them great at controlling pests and reducing the spread of pathogens like West Nile and Zika. The big brown bat, the largest species caught in The Preserve, eats up to 4,000 mosquitoes each night!
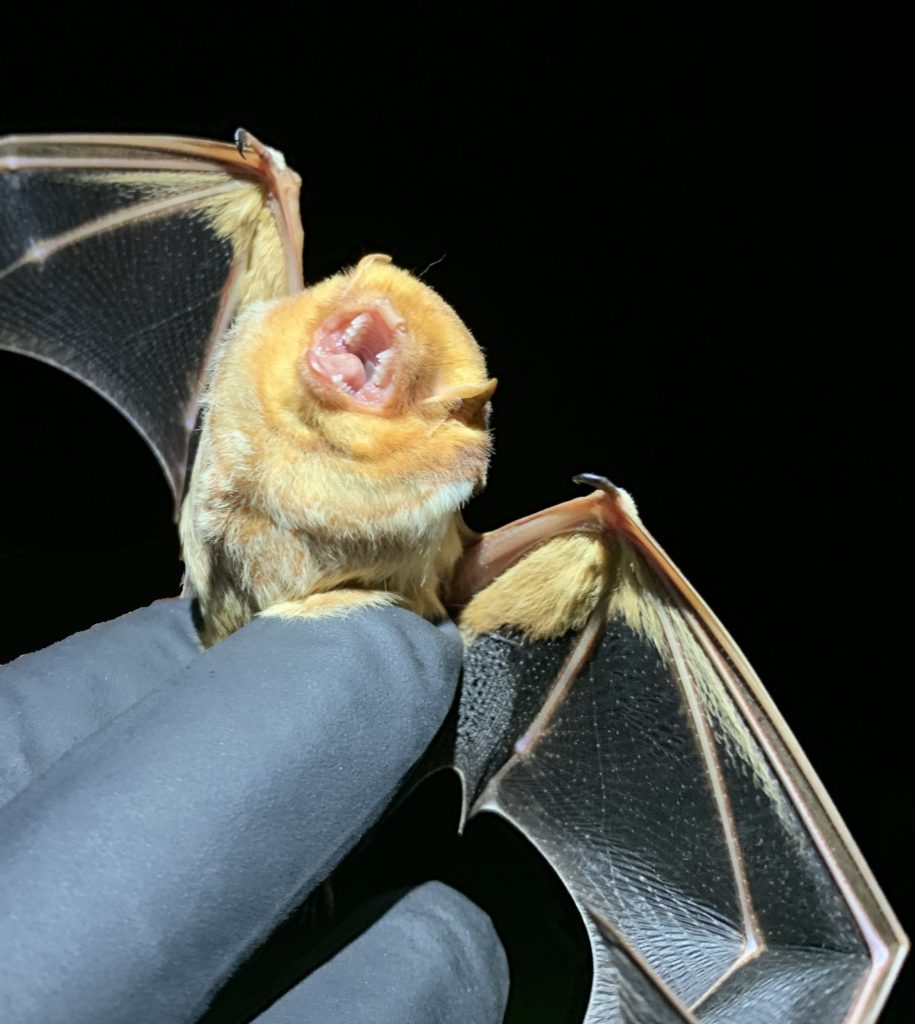

In early July, a private contractor surveyed The Preserve’s bat population by setting up 30 foot tall nets across various parts of our trails and creeks. We set up three nets every night, checking each of them every ten minutes between sunset and 2:00 a.m. In five days of netting we caught over 50 individuals representing five different species:
- Big brown bat (Eptesicus fuscus) – one of the largest and most common species in Kentucky, associated with man-made structures.
- Red bat (Lasiurus borealis) – a common, forest-dwelling species, roosting in trees instead of caves.
- Gray bat (Myotis grisescens) – listed as a threatened species in Kentucky and an endangered species federally, this cave-dwelling species migrates between breeding caves in the summer and hibernation caves in the winter.
- Small-footed bat (Myotis leibii) – a tiny, state threatened species, associated with cliffs.
- Evening bat (Nycticeius humeralis) – listed as a species of ‘special concern’ in Kentucky, primarily roosting in trees.
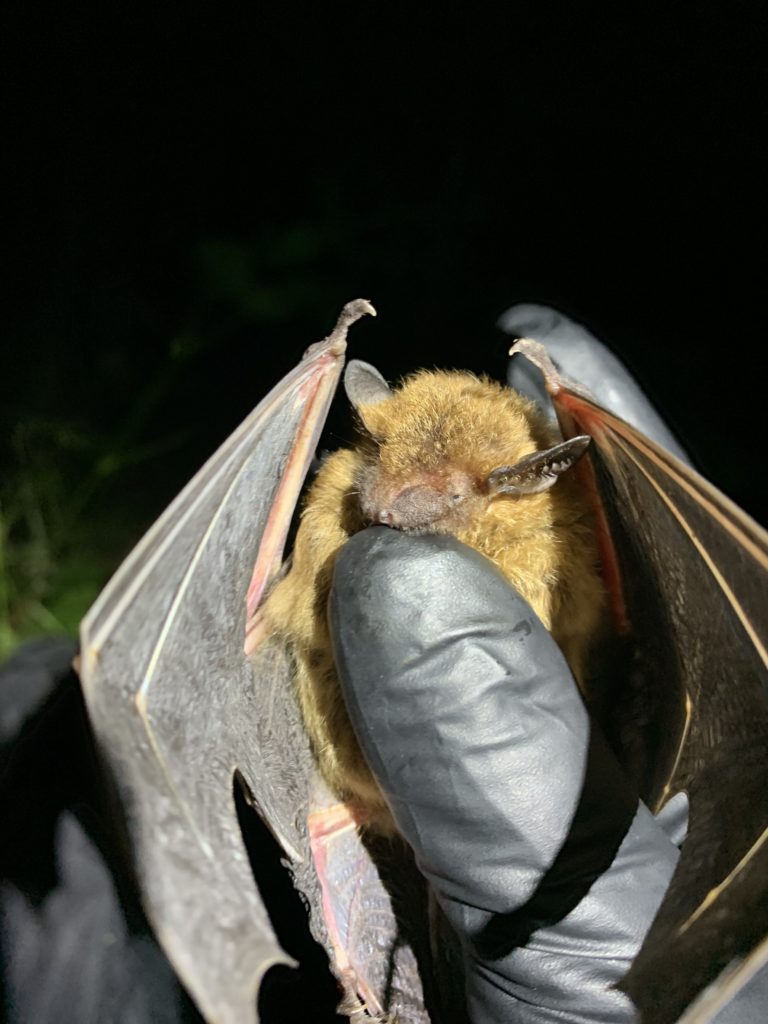

Big Brown Bat (Eptesicus fuscus) 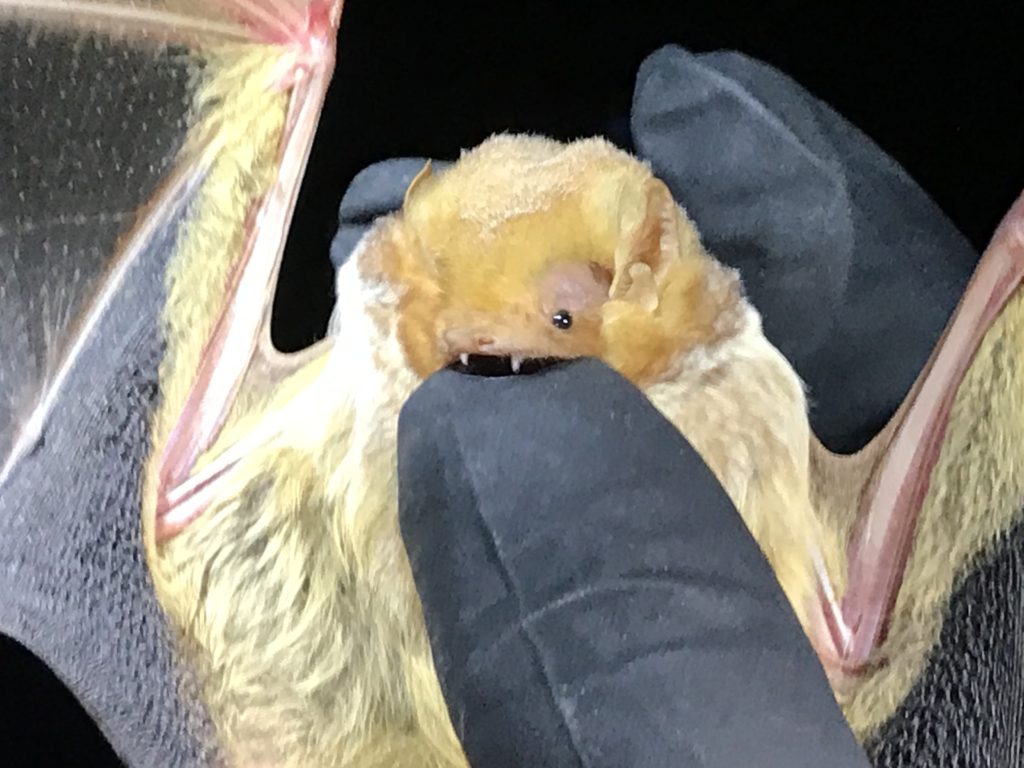
Close-up of Red Bat (Lasiurus borealis)
Interestingly, our most endangered species was the most commonly caught – over 40% of our caught bats were gray bats!

Up next for the Preserve Team is migration songbird banding. This helps us determine which bird species utilize our habitat as a refueling station for their trip south of the border for winter. To ensure the health of the birds, this event is not open to the public. Don’t worry, we take lots of pictures to share!



